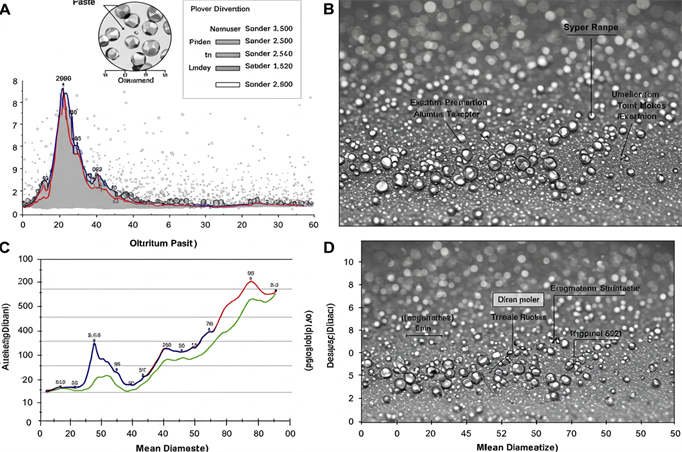
Have you ever opened a can of metallic paint and wondered why one batch looks like liquid chrome while another feels like scattered glitter? The secret is hidden in a simple curve called the Размер частиц алюминиевой пасты distribution. At Five Star New Materials, we like to think of this curve as the “personality chart” of every aluminum paste we make. A narrow peak on the left (tiny flakes, 1–10 µm) behaves like a tidy introvert—quiet, uniform, and great at hiding whatever is underneath. A broad hill on the right (larger flakes, 30–80 µm) acts like an exuberant extrovert—loud, flashy, and perfect when you want a bold sparkle that flips from silver to charcoal as you walk by.
Why does this matter to you? Because once you understand the language of particle size, you can pick the exact “personality” your coating, ink, concrete, or solar cell needs without costly trial-and-error. In the next few minutes, we’ll walk you through real-life examples: how a 5 µm Размер частиц алюминиевой пасты turns an auto-repair spray into mirror-like chrome, why 60 µm flakes make lightweight concrete float yet stay strong, and why our lab always checks D10, D50, and D90 before any batch leaves the Five Star plant. No jargon, no heavy math—just clear pictures and straight talk from the engineers who make the paste. Grab a coffee, scroll down, and let’s decode that curve together.
At Five Star New Materials, we recognize that the particle size of aluminum paste is a key factor that determines its performance across various applications. It influences everything from the shimmer in your paint to the efficiency of your solar cells. Let’s explore how.
How Aluminum Paste Particle Size Distribution Influences Coating Performance
The particle size distribution of aluminum paste significantly impacts coating performance in several ways:
- Hiding Power and Tinting Strength: Smaller particle sizes mean more aluminum flakes per unit volume, resulting in stronger hiding power and tinting strength. Этот creates a denser coating and a whiter color. Larger particle sizes reduce hiding power but enhance the “flop effect,” making the metallic sparkle more pronounced.
- Surface Gloss and Roughness Fine-grain aluminum paste (e.g., 5μm) produces a delicate, high-gloss coating, ideal for electroplated silver effects. Coarse-grain aluminum paste (e.g., 35μm) results in a strong granular feel and increased roughness, perfect for textured or sand-silver metallic coatings.
- Flash and Metallic Feel A wide particle size distribution (a mix of fine and coarse particles) enhances the flash effect but may reduce uniformity. A narrow particle size distribution (e.g., a small D90-D10 range) provides a more uniform metallic feel and better visual consistency.
- Excessively fine aluminum powder (e.g., < 10 μm) exhibits poor electrical properties, resulting in low transfer efficiency and nozzle clogging in electrostatic spraying. Overly coarse aluminum powder (e.g., > 90 μm) requires longer melting times, which can potentially cause orange peel or poor leveling. We recommend an optimal particle size range of 20–80 μm for electrostatic spraying and a D50 of 20–25 μm for water-based systems.
- Functional Performance (e.g., Heat Insulation, Corrosion Protection) For solar heat reflective coatings, coarse aluminum powder between 50–70 μm offers the highest reflectivity; however, we must balance this with application performance. In anti-corrosion coatings, fine aluminum powder (<15μm) forms a dense barrier, enhancing protective properties.
Summary and Recommendations
| Application Requirement | Recommended Particle Size Range | Distribution Requirement |
| High Coverage, Electroplating Silver Imitation | 5–10 µm | Narrow distribution (D90-D10 small) |
| Metallic Flash Effect | 15–25 µm | Medium distribution |
| Sand Silver Texture | 30–50 µm | Moderately wide distribution |
| Electrostatic Spray Powder Coating | 20–80 µm | <10µm particles <10% |
To optimize your process, we recommend a comprehensive evaluation of the particle size distribution using D10, D50, and D90 values, which can be precisely measured with a laser particle size analyzer.
Aluminum Paste Particle Size: A Core Parameter
The particle size (diameter) of aluminum paste is a key parameter that determines its application performance. Different particle size ranges of aluminum paste exhibit significant differences across various applications, including coatings, inks, building materials, and electronics. Here’s a systematic summary based on current data:
Aluminum Paste Particle Size Range and Classification
| Тип | Диапазон размеров частиц (D50) | Morphological Characteristics | Типичные области применения |
| Ultra-fine Aluminum Paste | 1–10 µm | Thin flakes, 0.1–0.5 µm thick | High-coverage electroplating imitation, automotive refinish paints, fine inks |
| Medium-Grain Aluminum Paste | 10–25 µm | Silver dollar or cornflake-like | Metallic flake paints, plastic paints, coil coatings |
| Coarse-Grain Aluminum Paste | 25–50 µm | Large flakes, irregular edges | Sand silver effect, architectural exterior walls, roof reflective coatings |
| Extra-Coarse Aluminum Paste | 50–100 µm | High aspect ratio flakes | Heat-insulating coatings, heavy-duty anti-corrosion primers |
Impact of Particle Size on Coating Performance
| Performance Dimension | Fine Particle Size (e.g., 5–10 µm) | Coarse Particle Size (e.g., 30–50 µm) |
| Hiding Power | High (more flakes per unit volume) | Low (requires higher additive amount) |
| Металлический блеск | Fine and soft, similar to electroplating effect | Strong sparkle, significant color shift with angle |
| Шероховатость поверхности | Low (suitable for high-gloss topcoats) | High (suitable for textured or matte systems) |
| Applicability | May clog spray guns (electrostatic spraying requires <10% ultra-fine powder) | Poor leveling, requires adjustment of spraying parameters |
| Functional Add-ons | Suitable for high reflectivity (e.g., LED heat dissipation inks) | Suitable for heat insulation (e.g., roof reflective coatings) |
Typical Product Examples (Industrial Grade)
We offer specialized aluminum pastes like the Bisley series:
- 108B type: D50 = 13–18 μm, ideal for lightweight concrete (density 150–350 kg/m³).
- 608B type: D50 = 38–42 μm, designed for high-expansion building materials.
And the Toyo Aluminum TFH series:
- TFH-A05P: D50 = 5 μm, perfect for high thermal conductivity heat dissipation adhesives.
- TFH-A30P: D50 = 30 μm, used in heat dissipation sheets.
Selection Recommendations
For high hiding power needs (like mobile phone casing paints), choose our D50 = 6–12 μm silver dollar-type aluminum paste. For metallic flash effects (like automotive refinish paints), select our D50 = 15–25 μm paste with a narrow distribution (D90-D10 < 20 μm). For anti-corrosion or heat insulation, opt for our D50 = 30–50 μm, pairing it with either floating or non-floating treatment to enhance directional alignment.
Suppose you require further application matching (such as water-based/solvent-based systems, or buoyancy control). In that case, we can adjust based on the specific product’s surface treatment (e.g., silica coating) and solvent compatibility.
Aluminum Paste Particle Size for Solder Paste
When using aluminum paste in solder paste, particle size control directly affects welding performance, wettability, printing stability, and final joint quality. Based on current public patents and product data, the typical range and requirements for aluminum paste particle size in solder paste are as follows:
Aluminum Paste Particle Size Range for Solder Paste
| Тип | Диапазон размеров частиц (D50) | Описание |
| Medium-Temperature Aluminum-Based Solder Paste | 1–200 µm | We prepare this solder powder from Al-Si-Cu-Ge alloys using gas atomization, and we control its particle size distribution through sieving. |
| Aluminum-Tin Solderable Paste | 0.5–3 µm (aluminum) | We use this in electronic soldering or solar busbar connections. Its ultra-fine aluminum powder enhances sintering activity and electrical conductivity. |
| Commercial Aluminum Solder Paste | 25–45 µm (tin alloy) | This includes products like Chip Quik SMDAL aluminum solder paste, which uses Grade T3 alloy powder suitable for dispensing and screen printing. |
Impact of Particle Size on Solder Paste Performance
| Performance Dimension | Fine Particle Size (e.g., 1–10 µm) | Coarse Particle Size (e.g., 25–45 µm) |
| Wettability | Reacts more easily with flux, enhancing wetting and spreadability | Requires higher temperatures for activation, slower wetting speed |
| Printing Precision | Suitable for fine-pitch printing, but prone to agglomeration and clogging screens | Suitable for conventional pitches, good printing stability |
| Solder Voids | Smaller particles melt quickly, reducing voids | Larger particles can melt unevenly, potentially introducing voids |
| Joint Strength | Fine particles sinter densely, resulting in high strength | Coarse particles may lead to interfacial discontinuities, slightly lower strength |
| Process Window | Temperature-sensitive, narrow process window | Wide process window, suitable for manual or hot air soldering |
Process Recommendations
For aluminum-based solder paste (e.g., Al-Si-Cu-Ge), we recommend controlling D50 between 20–75 μm, balancing fluidity and activity. For aluminum-tin paste used in electronic soldering, the aluminum powder particle size should be ≤3 μm, and the tin powder particle size 5–10 μm, ensuring good welding with copper tape after sintering. For SMT patch aluminum solder paste, we recommend T3 grade tin alloy powder (25–45 μm), compatible with standard steel mesh printing.
Summary of Selection Recommendations
| Application Scenario | Recommended Aluminum Paste Particle Size | Notes |
| Aluminum Radiator Soldering | 25–45 µm | We recommend using Sn96.5/Ag3.5 alloy solder paste. |
| Solar Busbar Aluminum Electrode | 0.5–3 µm | This requires a complementary sintering process. |
| Medium-Temperature Aluminum Alloy Brazing | 20–75 µm | We utilize Al-Si-Cu-Ge alloy, produced by gas atomization. |
To further optimize printing or welding performance, we advise a comprehensive evaluation that combines particle size distribution (D10/D50/D90) with surface coating treatment (e.g., flux compatibility).
Aluminum Paste Particle Size for Solar Cells
In solar cells (especially crystalline silicon cells), the particle size of backfield aluminum paste and aluminum powder is a critical parameter influencing sintering quality, contact resistance, warpage, and conversion efficiency. Based on current mainstream patents and industrial practices, we recommend the following particle size ranges and control points:
Industrial Grade Solar Cell Aluminum Paste Particle Size Specifications
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Объяснение |
| D50 (Median Diameter) | 4.5–7.5 µm | We’ve found this range balances sintering activity and film compactness while preventing over-sintering or aluminum blistering. |
| Dmax (Maximum Diameter) | ≤20 µm | Keeping the maximum particle size within this limit prevents screen clogging during printing, rough surfaces after sintering, or the precipitation of aluminum beads. |
| Particle Size Distribution Span | (D90–D10)/D50 < 1.5 | This ensures dense packing and a smooth, flat film after sintering, which significantly reduces warping. |
| Ultra-fine Powder Ratio | <2 µm particles comprise 1–10% | This proportion boosts early sintering activity and improves interfacial contact. However, too high a ratio can lead to aluminum blistering, so we carefully control this. |
| Particle Morphology | Spherical or Near-Spherical | Spherical particles facilitate dispersion and provide excellent printing fluidity, with a sphericity of ≥0.85. |
| Oxygen Content | <650 ppm | Maintaining low oxygen content results in a thinner oxide layer, which lowers contact resistance and significantly improves electrical conductivity, crucial for efficient current flow in applications like solar cells. |
Impact of Particle Size on Cell Performance
| Performance Dimension | Fine Particle Size (<5 µm primary) | Medium-Coarse Particle Size (5–10 µm) |
| Sintered Film Density | We achieve a denser film with a smoother surface. | The film might be slightly rougher, requiring optimized glass frit matching. |
| Сопротивление контактов | This is low, which helps improve the Fill Factor (FF). | It’s moderate, requiring a balance with the sintering window. |
| Aluminum Blistering/Beading | More prone to occurrence; we must control the <2 µm particle proportion. | The risk is lower. |
| Silicon Wafer Warpage | More prone to warpage; requires glass frit CTE matching. | Warpage is less significant. |
| Conversion Efficiency | Theoretically higher, but requires precise process matching. | Offers better stability for industrial mass production, making it the mainstream choice. |
Actual Application Cases
One patent implementation example used nitrogen-atomized aluminum powder with an average particle size of 5.52 μm and Dmax ≤ 20 μm, achieving a cell conversion efficiency of 17.63% and warpage < 2 mm. Our environmentally friendly lead-free formula uses < 7 μm spherical aluminum powder. After sintering, the aluminum film exhibits no aluminum blisters and an adhesion of more than 10 N, meeting environmental regulations.
Selection Recommendations
For high-efficiency PERC/TopCon cells, we prioritize aluminum powder with a D50 of 5–7 μm, narrow distribution, and high sphericity, combined with lead-free glass powder. For conventional polycrystalline cells, we can extend the D50 to 6–9 μm, allowing a small amount of particles larger than 15 μm to reduce paste cost. To further match specific sintering curves (peak 760–820 °C) and silicon wafer thickness (< 180 μm), we recommend actual measurement of D10/D50/D90 in conjunction with warpage/efficiency correlation data.
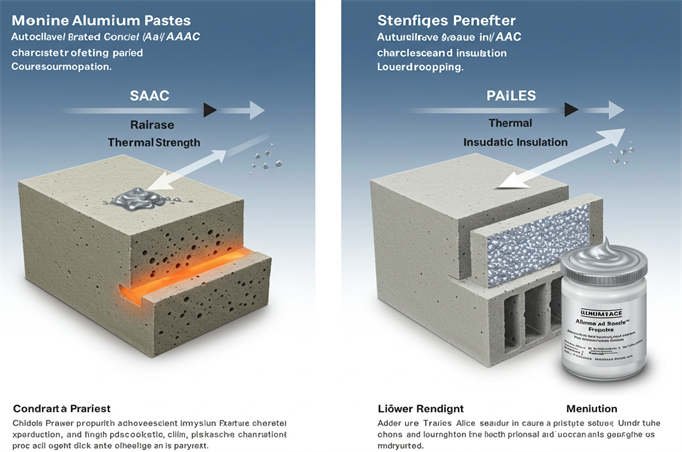
Aluminum Paste Particle Size for Autoclaved Aerated Concrete
На сайте Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) production, the particle size of the aluminum paste (aluminum powder paste) is a crucial factor determining the gassing effect, uniformity of pore structure, and final block performance. Based on the latest industry standards and actual process data, we recommend the following particle size ranges and control requirements:
Aluminum Paste Particle Size Requirements for Autoclaved Aerated Concrete
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Объяснение |
| D50 (Median Diameter) | 30–80 µm | Particles that are too fine can lead to overly rapid early gas evolution, while those too coarse can delay it, affecting the uniformity of the pore structure. |
| D97 (Maximum Particle Size) | ≤280 µm | This upper limit for raw material particle size comes from the dry ball milling process. |
| Распределение частиц по размерам | Narrow distribution, no coarse particles | This prevents uneven local gas evolution, which can cause fluctuations in block density or cracking. |
| Particle Morphology | Flaky or near-spherical | These shapes increase surface area, enhance reactivity with alkaline slurry, and promote uniform hydrogen gas release. |
| Содержание активного алюминия | ≥85% | This ensures effective gas evolution. Higher aluminum purity results in higher gas evolution efficiency. |
Impact of Particle Size on Aerated Concrete Performance
| Performance Dimension | Fine Particle Size (<30 µm) | Moderate Particle Size (30–80 µm) | Coarse Particle Size (>80 µm) |
| Gas Evolution Rate | Too fast, prone to mold collapse | Matches slurry thickening, uniform pore structure | Delayed gas evolution, prone to settling and stratification |
| Пористость | High, but uneven pore size | Uniform and fine pores, high closed-cell rate | Large pore size, reduced strength |
| Compressive Strength | Reduced (due to uneven pore structure) | Optimal (reasonable pore size distribution) | Reduced (large pores weaken the framework) |
| Dry Density Control | Highly variable | Stable (500–700 kg/m³) | Tends to be higher, difficult to achieve lightweight properties |
Process Recommendations
A typical aluminum powder paste formula includes 65% aluminum powder + 35% water (by mass). The addition amount is 0.05–0.08 wt% (based on dry material), which requires adjustment according to the aluminum powder’s activity and fineness. We recommend pre-treating the aluminum powder by degreasing and moisture-proofing to prevent surface oxide films from affecting gassing efficiency.
Summary of Selection Recommendations
| Application Scenario | Recommended Aluminum Paste Particle Size | Notes |
| Standard AAC Blocks | 30–80 µm | We find dry ball milling produces the best results, with an optimal D50 of approximately 50 µm. |
| Low-Density Insulation Blocks | Finer (30–50 µm) | This helps increase gas evolution and reduce density. |
| High-Strength Blocks | Coarser (60–80 µm) | We use this to control pore size and enhance structural strength. |
To further optimize the pore structure, you can synergistically use it in conjunction with surfactants or a composite gas system (such as hydrogen peroxide and aluminum powder).
Floating Aluminum Paste Particle Size
The particle size distribution of floating aluminum paste (also known as leafing aluminum paste) directly determines its floating properties, metallic luster, hiding power, and surface effect. Based on current mainstream product data, its particle characteristics are as follows:
Typical Particle Size Range
| Product Series | D50 (Median Diameter) | Max Particle Size | Описание |
| High-Gloss Chrome Type | 4–10 µm | ≤15 µm | We use this type to achieve a strong mirror-like effect. Finer particles ensure more stable floatation. It’s often applied in automotive reflectors and high-end metallic paints. |
| Standard Floating Type | 10–16 µm | ≤20 µm | This series balances hiding power with a metallic feel. We recommend it for marine coatings, roofing, and industrial protective paints. |
| Water-Based Floating Aluminum Paste | 7–13 µm | ≤15 µm | Featuring phosphate ester surface treatment, this is an eco-friendly option. We use it for rough surfaces like steel structures and болты. |
Impact of Particle Size on Performance
| Performance Dimension | Fine Particle Size (4–10 µm) | Medium Particle Size (10–16 µm) |
| Floatation Rate | High (driven by surface tension, stearic acid coating) | Moderate; requires control of solvent evaporation rate |
| Металлический блеск | Mirror-like/chrome effect | Silvery-white sparkle, stronger hiding power |
| Application Adaptability | Suitable for spray coating, dip coating; not ideal for brush coating | Suitable for brush coating, roller coating; higher film thickness tolerance |
| Scratch Resistance | Poor (exposed aluminum flakes) | Slightly better, but still requires clear coat protection |
Selection Recommendations
| Application Scenario | Recommended Particle Size (D50) | Product Example |
| Automotive Reflectors, Mirror Paints | 4–7 µm | Toyo 0870MS (D50=4 µm) |
| Marine, Roof Anti-Corrosion | 10–16 µm | Silberline W-500 (D50=13 µm) |
| Water-Based Eco-Friendly Coatings | 7–10 µm | Zuxing Water-Based Floating Series |
Important Considerations: The upper limit for particle size in floating aluminum paste must be ≤ 15 μm; larger particles will compromise floating stability. Stearic acid modification ensures floating properties, while phosphate ester modification improves compatibility with water-based systems. We recommend using low-polarity solvents (like MS/HA) and fast-drying resin systems to prevent aluminum flake settling. To further match specific coating systems (such as acrylic, alkyd, epoxy), we recommend a comprehensive evaluation that considers floating value (≥ 75%) and hiding power (cm²/g).
Non-Floating Aluminum Paste Particle Size
Non-floating aluminum paste has a wider particle size range than floating types, covering various decorative needs from fine electroplating imitation to coarse flashing silver, without the limitations of floating stability. Based on the latest product data and process descriptions, its typical particle size distribution is as follows:
Non-Floating Aluminum Paste Particle Size Spectrum
| Effect Category | D50 (µm) | Max Particle Size | Form/Morphology | Типичные области применения |
| Ultra-fine Electroplating Imitation | 8–12 µm | ≤15 µm | Silver Dollar | Automotive interiors, plastic casings, consumer electronics |
| Medium Electroplating Imitation | 15–25 µm | ≤30 µm | Silver Dollar | Automotive OEM paints, coil coatings |
| Medium-Coarse Sparkle | 27–43 µm | ≤45 µm | Silver Dollar/Flake | Architectural exteriors, high-decorative industrial topcoats |
| Coarse Flash Silver | 45–60 µm | ≤60 µm | Silver Dollar | Furniture, toys, signage coatings (prominent grain) |
Particle Size-Performance Relationship
- D50 ≤ 15 μm: Offers a delicate metallic feel and high hiding power, perfect for high-gloss “electroplating imitation” effects.
- D50 20–40 μm: Provides a uniform, subtle metallic flash, balancing hiding power and flop effect.
- D50 ≥ 45 μm: Exhibits a noticeable granular feel and strong sparkle, supporting coarse flash, sand-silver, and other special decorative finishes.
Differences from Floating Types:
Particle size upper limit: Non-floating types can reach 60 μm, while floating types are typically ≤ 15 μm to prevent floating failure. Distribution requirements: Non-floating types demand stricter control over large particles and impurities, ensuring uniform settling within the paint film and no aluminum blisters. Surface coating: We use oleic acid or resin coating to ensure stable distribution of aluminum flakes in the lower layers of the paint film, enhancing recoatability and scratch resistance.
Quick Selection Guide
| Demand Scenario | Recommended Particle Size | Product Examples |
| High-End Plastic Electroplating Imitation | 8–12 µm | TS9308 / TS9110 |
| Automotive Wheel Hub High-Brightness Sparkle | 15–25 µm | TS9124 / TS9317 |
| Architectural Curtain Wall Coarse Silver Flash | 30–45 µm | TS1625 / TS1641 |
| Furniture/Toy Granular Texture | 45–60 µm | Custom-grade non-floating coarse flash paste |
To further match specific resin systems (acrylic, polyurethane, epoxy, etc.) or environmental regulations (low VOC, no PAHs, water-based), select a non-floating aluminum paste with the corresponding surface treatment within the described particle size range.
Water-Based Aluminum Paste Particle Size
Water-based aluminum paste boasts a broad particle size range, primarily between 6 and 80 μm, with the most concentrated industrial application range being 6–40 μm. We can further categorize it based on specific effect requirements:
Key Process Control
Upper limit control: The vast majority of water-based aluminum pastes require 100% passage through a 45 μm wet sieve, ensuring no nozzle or screen clogging during spraying or printing.
| Effect Category | Typical D50 Particle Size | Characteristics & Applications |
| Fine White Silver | 6–12 µm | We use this for strong hiding power and a soft metallic feel, ideal for water-based automotive OEM paints and high-end plastic coatings. |
| Electroplating Silver Imitation | 8–18 µm | This provides an excellent mirror effect and high gloss, suitable for water-based automotive parts and consumer electronics casings. |
| Fine Flash Silver | 10–20 µm | We achieve a delicate sparkle and color shift with angle, perfect for water-based toys and packaging inks. |
| Medium Flash Silver | 20–30 µm | This delivers a noticeable metallic sparkle, used in water-based industrial paints and architectural curtain walls. |
| Coarse Flash Silver | 30–45 µm | We utilize this for a strong granular feel and significant visual impact, commonly found in water-based outdoor advertising and furniture coatings. |
Distribution requirements: High-end series (such as TW8100/8200) feature an ultra-narrow distribution, which reduces color differences and improves batch stability. Surface coating: We commonly use single-layer silica coating или double-layer silica + organic resin coating to enhance dispersion, anti-settling, acid-alkali resistance, and weatherability in water-based systems.
Quick Selection Guide
| Application System | Recommended Particle Size (D50) | Product Examples |
| Water-Based Automotive Refinish Paint | 8–12 µm | TW8108 |
| Water-Based Plastic Casing Electroplating Imitation | 10–16 µm | TW8116 |
| Water-Based Industrial Flash Paint | 22–28 µm | TW8428 |
| Water-Based Ink Fine Flash Effect | 6–14 µm | TW8409–8417 |
To further match specific water-based resins (such as acrylic, polyurethane, and epoxy) or environmental regulations (low VOC, APEO-free), select products within the described particle size range that correspond to the specified surface treatment grades.
The Right Particle Size for the Right Application
At Five Star New Materials, we see aluminum paste particle size as a “one key opens one lock” principle:
- Small particles (D50 1–10 µm) → High surface area, high activity → Conductivity, bonding, dense coatings
- Large particles (D50 30–80 µm) → Low surface area, low resistance → Gassing, pore size control, lightweight concrete
In other words: “Smaller particle sizes enhance performance, larger particle sizes create structure.” First, define your application goal, and then we will customize the particle size accordingly.
So, there you have it—the humble Размер частиц алюминиевой пасты curve is a roadmap to performance. Whether you need a whisper-thin, high-gloss phone case or a rugged solar-cell back-sheet that never warps, the right dot on that graph makes the difference between “good enough” and “five-star perfect.” At Five Star New Materials, we don’t just sell aluminum paste; we sell the confidence that every gram matches the story you promised your customer. Our laser diffractors run 24/7, our surface-coat teams tweak silica layers in nanometers, and our logistics crew ships worldwide with sealed certificates that show the exact D10, D50, D90 your QC manager loves to see.
Next step? Reach out and tell us what your end-product must do—reflect, protect, insulate, or look stunning. In under 48 hours, we’ll translate your words into the precise blend of aluminum paste particles and surface treatment you need. Because at Five Star, the curve is not just data; it’s our handshake with you. Thank you for reading.
We look forward to making your next project shine, just the way you imagined it.
FAQ – Aluminum Paste Particle Size
1. What is the best aluminum paste particle size for a mirror-like chrome finish on plastic parts?
Use a non-leafing grade with D50 = 6–12 µm and a narrow distribution (D90–D10 < 15 µm). The small, uniform flakes lay flat and reflect light like a mirror.
2. How does particle size affect solar-cell efficiency?
Finer particles (D50 ≈ 5–7 µm) sinter faster and form a dense back-surface field, lowering contact resistance and reducing wafer bow. Larger particles risk poor adhesion and higher series resistance.
3. Can I use coarse aluminum paste (>45 µm) in waterborne coatings?
Yes, but only if the flakes are silica-coated and the mill base is shear-stable. Above 45 µm, 100% must still pass a 45 µm wet screen to avoid spray gun clogging.
4. Which particle size gives the strongest “flip-flop” sparkle in automotive paint?
A bimodal blend—15 µm flakes plus 35 µm flakes—creates large sparkling spots that shift color as the viewing angle changes. Keep the coarse fraction below 40% to ensure smooth leveling.
5. Why does my electrostatic spray line lose powder when I switch to very fine aluminum (<10 µm)?
Sub-10 µm particles have poor charge acceptance and are easily swept away by the airflow. Move to 20–40 µm or add a small amount of coarse carrier powder to raise transfer efficiency.
6. Is bigger always better for lightweight concrete pore size?
Not exactly. To get uniform 0.5–1 mm pores in AAC blocks, choose D50 = 50–70 µm active алюминиевая пудра. Too coarse (>90 µm) results in late, uneven gas release; too fine (<30 µm) finishes too quickly and collapses the bubbles.